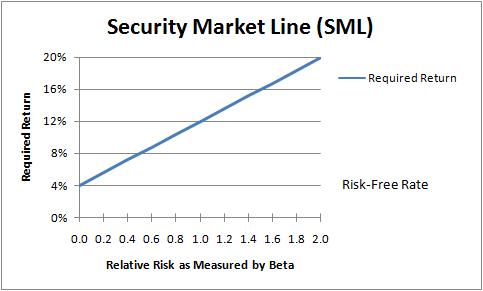
Security market line graphs
The security market line "SML" or "characteristic line" graphs the systematic or market risk versus the return of the whole market at a certain time and shows all risky marketable securities. The SML essentially graphs the results from the capital asset pricing model CAPM formula. The x-axis represents the risk beta , and the y-axis represents the expected return. The market risk premium is determined from the slope of the SML.
The security market line is a useful tool for determining whether an asset being considered for a portfolio offers a reasonable expected return for risk. Individual securities are plotted on the SML graph. If the security's risk versus expected return is plotted above the SML, it is undervalued because the investor can expect a greater return for the inherent risk. A security plotted below the SML is overvalued because the investor would be accepting less return for the amount of risk assumed.
Expected values for the SML are calculated with the following equation: It is the measure of the riskiness of a project. When taken in isolation, a project may be considered more or less risky than the current risk profile of a company. By using the SML as a means to calculate a company's WACC, this risk profile would be accounted for.
Daily Stock Market Forecast and predictions for with accurate Stock Market Timing Advice and ETF Trading Strategies Newsletter
When a new product line for Newco is considered, the project's beta is 1. Estimating Beta In risk analysis, estimating the beta of a project is quite important. But like many estimations, it can be difficult to determine.
The two most widely used methods of estimating beta are: Pure-Play Method When using the pure-play method, a company seeks out companies with a product line that is similar to the line for which the company is trying to estimate the beta. Once these companies are found, the company would then take an average of those betas to determine its project beta. Suppose Newco would like to add beer to its existing product line of soda.
Newco is quite familiar with the beta of making soda given its history. However, determining the beta for beer is not as intuitive since Newco as it has never produced it. To determine the beta of the new beer project, Newco can take the average beta of other beer makers, such as Anheuser-Busch and Molson Coors.
BSE2310-CAPM and IRR GraphThe accounting beta is the slope coefficient of the regression. The typical procedure for developing a risk-adjusted discount rate is as follows: A company first begins with its cost of capital for the firm. The cost of capital then must be adjusted for the riskiness of the project, by adjusting the company's cost of capital either up or down depending on the risk of the project relative to the firm. For projects that are riskier, the company's WACC would be adjusted higher, and if the project is less risky, the company's WACC is adjusted lower.
The main issue in this procedure is that it is subjective. Capital Rationing Essentially, capital rationing is the process of allocating the company's capital among projects to maximize shareholder return. When making decisions to invest in positive net-present-value NPV projects, companies continue to invest until their marginal returns equal their marginal cost of capital.
There are times, however, when a company may not have the capital to do this. As such, a company must ration its capital among the best combination of projects with the highest total NPV.
Security Market Line (SML)
Risk Premium At its most basic level, risk premium is the return in excess of the risk-free rate of return that an investment is expected to yield.
An asset's risk premium is a form of compensation for investors who tolerate the extra risk in a given investment compared to that of a risk-free asset. Think of a risk premium as a form of hazard pay for your investments. Just as employees who work in relatively dangerous jobs receive hazard pay as compensation for the risks they undertake, risky investments must provide an investor with the potential for larger returns to warrant taking on the additional liability.
For example, high-quality corporate bonds issued by established corporations earning large profits have very little risk of default. Therefore, such bonds will pay a lower interest rate or yield than bonds issued by less-established companies with uncertain profitability and relatively higher default risk.
Market Risk Premium Market risk premium is the difference between the expected return on a market portfolio and the risk-free rate. Market risk premium is equal to the slope of the security market line SML. Three distinct concepts are part of market risk premium: The historical market risk premium will be the same for all investors since the value is based on what actually happened.
The required and expected market premiums, however, will differ from investor to investor based on risk tolerance and investing styles. The market risk premium can be calculated as follows: The Equity Risk Premium: More Risk for Higher Returns In theory, stocks should provide a greater return than safe investments like Treasury bonds.
The difference is called the equity risk premium: There is vigorous debate among experts about the method employed to calculate the equity premium and, of course, the resulting answer. In this section, we take a look at these methods - particularly the popular supply-side model - and the debates surrounding equity premium estimates. Why Does It Matter? The equity premium helps to set portfolio return expectations and determine asset allocation policy.
A higher premium, for instance, implies that you would invest a greater share of your portfolio into stocks. Also, the capital asset pricing relates a stock's expected return to the equity premium; a stock that is riskier than the market - as measured by its beta - should offer excess return above the equity premium.
Greater Expectations Compared to bonds, we expect extra return from stocks due to the following risks: And history validates theory.
If you are willing to consider holding periods of at least 10 or 15 years, U. But history is one thing, and what we really want to know is tomorrow's equity premium.
Specifically, how much of a premium above a safe investment should we expect for the stock market going forward? Later in this article, we'll explain why this is always the conclusion of an academic study, whereas money managers often point to recent history and arrive at higher estimations of premiums. Getting at the Premium Here are the four ways to estimate the future equity risk premium: What a range of outcomes!
Opinion surveys naturally produce optimistic estimates, as do extrapolations of recent market returns. But extrapolation is a dangerous business: Professor William Goetzmann of Yale has cautioned, "History, after all, is a series of accidents; the existence of the time series since might itself be an accident.
Bond returns were low in part because bond buyers in the s and s - misunderstanding government monetary policy - clearly did not anticipate inflation. Dictionary Term Of The Day. A measure of what it costs an investment company to operate a mutual fund. Latest Videos PeerStreet Offers New Way to Bet on Housing New to Buying Bitcoin?
This Mistake Could Cost You Guides Stock Basics Economics Basics Options Basics Exam Prep Series 7 Exam CFA Level 1 Series 65 Exam. Sophisticated content for financial advisors around investment strategies, industry trends, and advisor education.
The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) and the Security Market Line (SML) — Valuation Academy
Security Market Line And Beta Basics By Investopedia Share. Chapter One Chapter Two Chapter Three Chapter Four Chapter Five. Think of a risk premium as a form of hazard pay for risky investments. Learn how the bet against beta strategy is used by a large hedge fund to profit from a pricing anomaly in the stock market caused by high stock prices. Market risk premium is equal to the expected return on an investment minus the risk-free rate. The risk-free rate is the minimum rate investors could expect to receive on an investment if it Equity risk premium is the excess expected return of a stock, or the stock market as a whole, over the risk-free rate.
CAPM helps you determine what return you deserve for putting your money at risk.
Learn how the expected extra return on stocks is measured and why academic studies usually estimate a low premium. The required rate of return is used by investors and corporations to evaluate investments. Find out how to calculate it. Beta says something about price risk, but how much does it say about fundamental risk factors?
Despite several drawbacks, the CAPM gives an overview of the level of return that investors should expect for bearing only systematic risk. Applying Apple, we get annual expected return of about Traditionally, historical quotes on stocks and indexes were hard to come by for the general public, but this is no longer You may participate in both a b and a k plan.
However, certain restrictions may apply to the amount you can Generally speaking, the designation of beneficiary form dictates who receives the assets from the individual retirement Content Library Articles Terms Videos Guides Slideshows FAQs Calculators Chart Advisor Stock Analysis Stock Simulator FXtrader Exam Prep Quizzer Net Worth Calculator.
Work With Investopedia About Us Advertise With Us Write For Us Contact Us Careers. Get Free Newsletters Newsletters. All Rights Reserved Terms Of Use Privacy Policy.